BesSystem
build fast in safely and quality
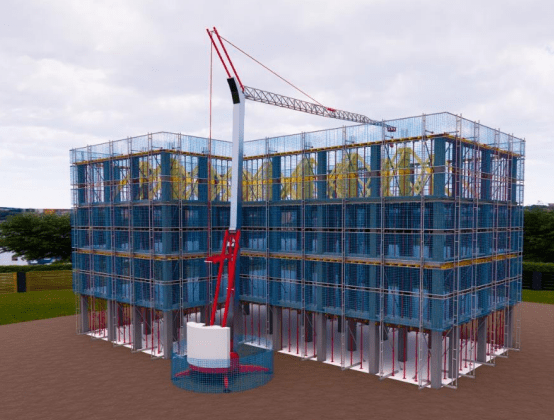



Bessystem is a system designed for the protection of full-height edges designed
and studied for new buildings that develop mainly in height.
Bessystem was born from the 30 years of experience of the Brembo International
team and two years of R&D. It was born from the idea of avoiding the use of
scaffolding in new constructions, in order to be able to work in complete safety
with the great advantage that it reduces time and costs thanks to its lightness,
simplicity, adaptability and speed in assembly.
The reference regulations are:
EN 13374 (2013) – Temporary edge protection system – Product specification –
Test method.
EN 1993 – Eurocode 3 (series) – Design of steel structures.
EN 1999 – Eurocode 9 (series) – Design of aluminum structures.
The supplementary technical documents:

CNR-DT 208/2011 –
Instructions for the Design,
Execution and Control of
Aluminum Structures.
WD EN 13374:2021 (E) – text
final revision phase EN13374
(CEN/TC 53/WG 10 N 196).
EN 74 (series) – Couplers,
spigot pins and baseplates for
use in falsework and scaffold.
EN 1004 – Mobile access and
working towers made of
prefabricated elements –
Materials, dimensions, design
loads, safety and performance
requirements.
EN 12810 (series) – Facade
scaffolds made of prefabricated
components.
EN 12811 (series) – Temporary
works equipment.
Are you looking for a company that specializes in the assembly of fall protection nets and sheets but you don’t know who to turn to? Brembo International, based in Bergamo, but also present in Milan, Verona, Turin and Brescia, is able to offer you services perfectly in line with your needs.
Bessystem has been certified by a calculation report and by a third-party Spanish
certification body called Tecnalia.
This report document relates to the static checks during the assembly and
operation phase of an aluminum and steel structure constituting, together with
protective nets, a safety barrier for operators working at heights.
The report does not deal with general and functional operational safety criteria,
but only, starting from the general project, examines the overall structural aspects
of the metal components of the protection structure. Verifications for Class A
protections (according to EN13374) are examined by subsets. For dynamic tests
relating to Class B protections, please refer to the specific test reports.
Installation from the ground on shelves with partial overhang is taken into
consideration, overlapping three modules of uprights (1.8m + 3m + 3m) especially
for checking the base steel shelf. Subsequent models take into consideration the
extraction of the basic module (1.8m upright) and therefore of the base bracket
and the evaluation of the load-bearing capacity of up to five upper floors supported
by steel brackets whose insertion is cast into the reinforced concrete curb. of the
attics.
The height of the floor boards is considered equal to 4m for the first one from the
ground then 3.5m for the subsequent ones. Obviously lower heights are favorable.
In this overall phase of the five floors, in favor of safety, it is considered that the
weight of the five floors of the upper protection structure is supported, for issues
related to the geometric assembly clearances, by the three levels of the lower
shelves without considering the two levels superiors as operating as support. All
the brackets, however, will be operational for locally horizontal loads. The shelf
structures are made of steel. The vertical and horizontal structures supporting the
nets are made of Aluminum.
Φ diameter
The horizontal structures are made of Φ 50×3 aluminum tubing. In the two overall models, for simplicity and easier interpretation, half horizontal elements have been inserted. To simulate the weight of the crosspieces and the net, in the overall models for the transfer of vertical loads, the horizontal elements are simulated with a Φ50×8 tube as reported below. The capacities of the Φ 50×3 tube are evaluated separately, as a subset.
The support brackets of these beams on the uprights and of the double tubular Φ50×2 uprights and crosspieces also in Φ 50×2 assembled to form a Vierendeel type beam are also evaluated and verified separately. The overall modeling aims to evaluate all the possible situations that can occur on a construction site.
Simulation of a building with an irregular plan with the protection uprights starting at 0.7m from the top itself. Variable steps with a maximum step of 3m as foreseen by the project. Situations in which a protective wall is made up of only two uprights etc. The horizontal beams are also positioned with overlap in length (in the two bracket slots) according to their standard lengths. In favor of safety, the external vertices, although foreseen in the project connected by two clamps and connecting rod, in the model have not been connected but are free from each other.
Φ diameter
The horizontal structures are made of Φ 50×3 aluminum tubing. In the two overall models, for simplicity and easier interpretation, half horizontal elements have been inserted. To simulate the weight of the crosspieces and the net, in the overall models for the transfer of vertical loads, the horizontal elements are simulated with a Φ50×8 tube as reported below. The capacities of the Φ 50×3 tube are evaluated separately, as a subset.
The support brackets of these beams on the uprights and of the double tubular Φ50×2 uprights and crosspieces also in Φ 50×2 assembled to form a Vierendeel type beam are also evaluated and verified separately. The overall modeling aims to evaluate all the possible situations that can occur on a construction site.
Simulation of a building with an irregular plan with the protection uprights starting at 0.7m from the top itself. Variable steps with a maximum step of 3m as foreseen by the project. Situations in which a protective wall is made up of only two uprights etc. The horizontal beams are also positioned with overlap in length (in the two bracket slots) according to their standard lengths. In favor of safety, the external vertices, although foreseen in the project connected by two clamps and connecting rod, in the model have not been connected but are free from each other.
Having then identified the most stressed shelf in the corbels from the floors
(second model), the accidental load condition was considered in the same position
(Fd = 125daN vertical) to verify the typical corbel in two positions (mid horizontal
current span and position near to the upright). The fall of a person was also
simulated, a fall actually caused by the damping deformation of the net, in the area
where the net was rotated towards the inside of the shelf for approximately 0.5m.
A weight of 80kg with a dynamic coefficient of 1.5 was adopted. Therefore a total
of 120kg divided (30kg) on four support points of the relevant crosspieces, two
external upper parts supporting the net and two lower internal parts of the relative
shelf.
In the ground model, for design consideration even if essentially non-operational in the absence of horizontal loads, for each upright, the internal stay anchored to the upright and to the floor was installed.
The assembly criterion is that the stays on the plane in question must always be placed in the absence of the effectiveness (therefore of the casting) of the bracket of the relatively upper plane.
In conclusion, in the report from the checks carried out it essentially emerges that the Besssystem protection system must have support at the base on the ground floor until, above, there are three floors with cast and effective shelves. Only when there are four levels of cast and effective shelves will it be possible to remove the ground support and have support only from the floor shelves.
In the ground model, for design consideration even if essentially non-operational in the absence of horizontal loads, for each upright, the internal stay anchored to the upright and to the floor was installed.
The assembly criterion is that the stays on the plane in question must always be placed in the absence of the effectiveness (therefore of the casting) of the bracket of the relatively upper plane.
In conclusion, in the report from the checks carried out it essentially emerges that the Besssystem protection system must have support at the base on the ground floor until, above, there are three floors with cast and effective shelves. Only when there are four levels of cast and effective shelves will it be possible to remove the ground support and have support only from the floor shelves.
Quick Links
Copyright © Studio Belmont 2024 All Rights Reserved Privacy Policy

